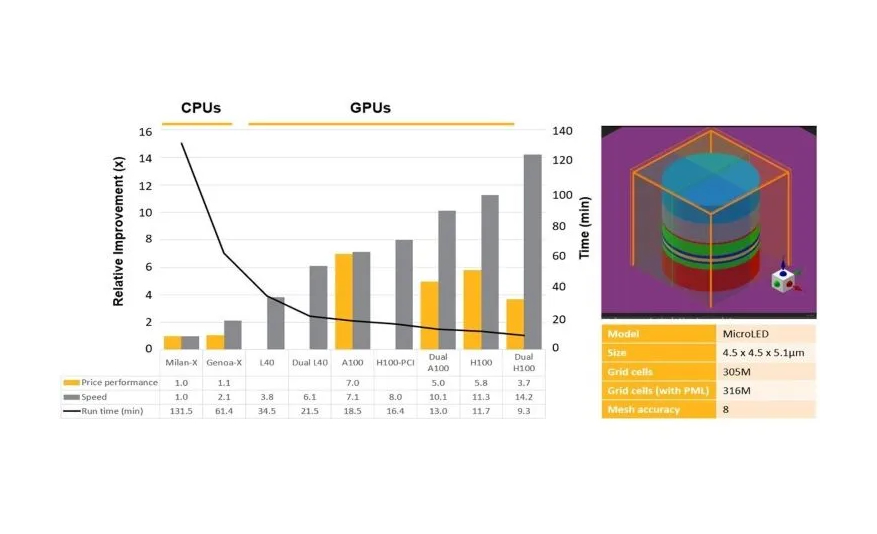
Ansys Inc., Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co. Ltd. (TSMC), and Microsoft Corp. are collaborating to speed up the simulation and analysis of silicon photonic components.
Together, the companies achieved over 10X speed-up of Ansys Lumerical FDTD photonics simulation via Microsoft Azure NC A100v4-series virtual machines, powered by NVIDIA accelerated computing running on Azure AI infrastructure. PICs are integral to applications across industries, including data communications, biomedical tools, automotive LiDAR systems, artificial intelligence, and more.
Silicon PIC, a type of optical communications that enables data to travel farther and faster, is integral to hyperscale data centers and Internet-of-Things applications. Combining photonic and electronic circuits is a painstaking task requiring precise multiphysics design and fabrication. A minor misstep can create continuity challenges within chips, which can result in added cost and timeline setbacks up to several months.
To alleviate challenges and unlock the ultra-bandwidth capabilities of silicon PIC, TSMC collaborated with Ansys to speed-up Lumerical FDTD simulations using highly efficient Azure virtual machines that use NVIDIA GPUs. Azure NC A100v4 VMs executed the simulations and identified optimal resources that balance cost with performance. The overall result is seamless deployment, graphical interface access, scaling of distributed simulations, and post processing for large datasets in cloud environments. For a consistent end-to-end digital engineering workflow, Azure Virtual Desktop provided a seamless transition to the cloud by delivering the same user experience as on a desktop.
“The size and complexity of our multiphysics silicon solutions makes the process of simulating all possible parameter combinations challenging. This latest collaboration again highlights that Ansys effectively harnesses the latest cloud infrastructure and techniques to deliver powerful, predictively accurate solutions that produce results in a fraction of the time,” said Stefan Rusu, head of silicon photonics system design at TSMC.
Deploying Lumerical FDTD on the cloud enables designers to swiftly identify optimal chip designs that account for the multiphysics challenges related to combining photonic circuits with electronic circuits.
“Ansys has developed unique capabilities that can be closely coupled with our leading multiphysics simulation engines for photonics. Collaborating with TSMC and Microsoft has accelerated technologies that address high-speed optical data transfer, which is one of the most important chip design challenges today,” said John Lee, vice president and general manager of the semiconductor, electronics, and optics business unit at Ansys.
Shelly Blackburn, CVP of Azure Infrastructure, Digital and App Innovation at Microsoft, highlighted the benefits of the ongoing collaboration with Ansys and TSMC. “Our collaboration is a significant advantage for users seeking the combined power of HPC and AI, using the flexibility of cloud solutions while maintaining the familiar on-premises experience. By working together, we aim to address the complexities of large-scale designs essential for high-quality semiconductor products. Utilizing the power and scalability of Microsoft Azure’s cloud computing is a key strategy in overcoming these challenges,” she said.